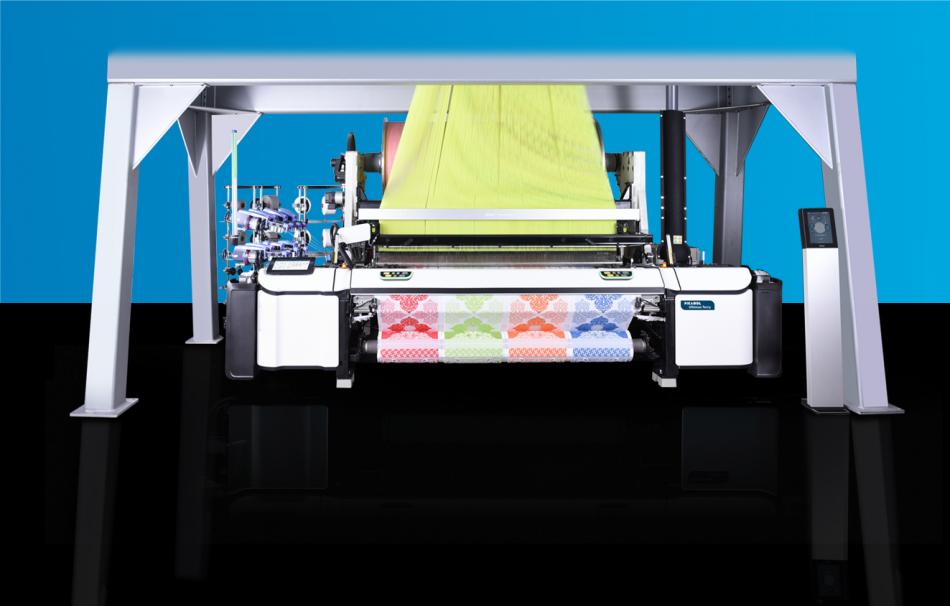
Picanol, highlights global shift toward air‑consumption optimization in weaving mills for 2026

Weaving mills from Europe to South Asia are cutting compressed-air use with data-driven monitoring, leak audits and airflow-balancing routines.
A new industry analysis compiled with data from Picanol’s global user base shows that weaving mills across Europe, Türkiye, the Middle East and South Asia have intensified their focus on air‑consumption reduction as energy tariffs fluctuate through late 2025. The shift reflects a broader movement toward production models designed around energy transparency, stable operating costs and measurable environmental impact.
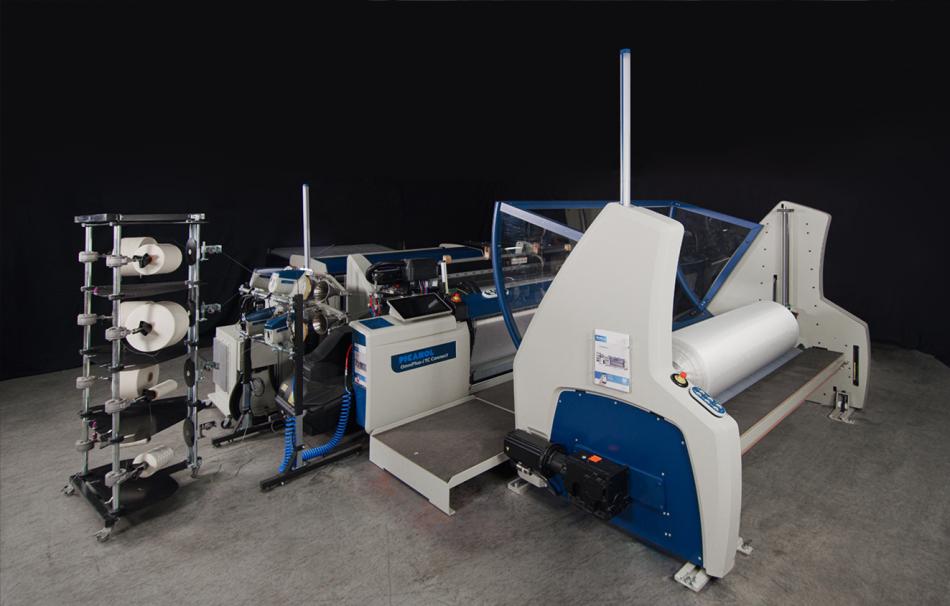
The report indicates that air‑jet weaving users recorded the highest efficiency gains when combining nozzle‑pressure mapping, pipeline maintenance cycles and airflow‑balancing routines. Several mills in Türkiye and Italy reported double‑digit reductions in monthly compressed‑air costs after implementing structured monitoring routines across all shifts.
Weaving teams adopt advanced diagnostic practices
According to the findings, mills increasingly rely on digital diagnostic tools to detect pressure drops, valve fatigue and unbalanced air routes before they lead to unnecessary consumption. Engineers noted that the most effective strategies integrate routine air‑leak audits, stable compressor zoning and simplified cleaning tasks that reduce turbulence inside pipelines. Some factories introduced cross‑shift dashboards during November and December, enabling supervisors to compare real‑time air profiles across loom groups. Early pilot users reported fewer pressure deviations and more predictable energy planning during fast‑style‑change operations.
Energy‑cost volatility accelerates optimization strategies
In regions where energy prices changed frequently throughout the year, weaving plants shifted from “reactive maintenance” to data‑supported, continuous optimization. Picanol’s analysis shows that operators who standardized airflow‑balancing sequences achieved smoother filling insertion and fewer micro‑stoppages during demanding yarn combinations. Several weaving clusters in Southeast Asia and North Africa began applying weekly airflow‑uniformity checks, encouraging teams to track small deviations that accumulate into higher‑than‑expected electricity use. Managers reported that these routines supported more stable loom groups and reduced the load on older compressor installations.
Sustainability targets shape new weaving priorities
Brands requesting clearer environmental metrics pushed many mills to document air‑use efficiency more transparently. As reporting frameworks expand in 2026, analysts expect air‑consumption monitoring to become a central performance indicator, influencing purchasing decisions and production‑planning strategies.
Industry observers emphasize that the shift toward optimization represents a long‑term evolution rather than a short‑term cost reaction. With energy‑intensive weaving markets under stronger scrutiny, mills adopting structured air‑management routines are expected to maintain competitive advantages through 2026 and beyond.